What is Predictive Analytics ?

What is Predictive Analytics ?
Predictive analytics is a branch of advanced analytics that utilizes historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to forecast future events or behaviors. By identifying patterns and relationships within data, organizations can make informed decisions and anticipate outcomes.
Key Features of Predictive Analytics :
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant historical and current data from various sources.
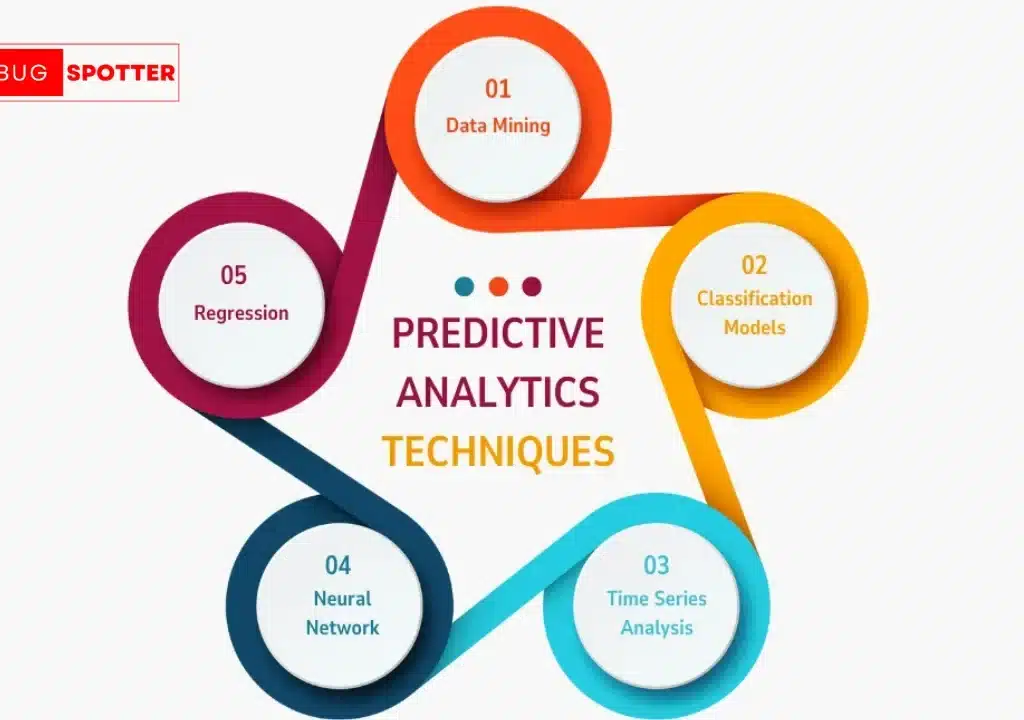
- Data Mining: Exploring datasets to identify patterns and relationships.
- Statistical Modeling: Applying statistical techniques to develop predictive models.
- Machine Learning: Utilizing algorithms that learn from data to improve predictions over time.
- Predictive Modeling: Creating models that forecast future outcomes based on identified patterns.
How to Use Predictive Analytics :
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline the goals of the analysis.
- Collect Data: Gather relevant data from internal and external sources.
- Data Preparation: Clean and preprocess the data to ensure accuracy.
- Select Modeling Technique: Choose appropriate statistical or machine learning models.
- Model Building: Develop and train the predictive model using the prepared data.
- Validation: Test the model’s accuracy using a subset of data.
- Deployment: Implement the model to make predictions on new data.
- Monitoring: Continuously assess the model’s performance and update as needed.
Importance of Predictive Analytics :
- Informed Decision-Making: Provides data-driven insights for strategic planning.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies potential risks and allows for proactive measures.
- Resource Optimization: Helps allocate resources efficiently based on predicted needs.
- Competitive Advantage: Enables organizations to stay ahead by anticipating market trends.
Applications of Predictive Analytics :
| Industry | Application Example |
|---|---|
| Finance | Assessing credit risk and detecting fraudulent activities. |
| Healthcare | Predicting disease outbreaks and patient admissions. |
| Marketing | Optimizing campaigns by understanding customer behavior. |
| Manufacturing | Forecasting demand and managing resources. |
Is AI Predictive Analytics ?
AI predictive analytics uses machine learning, statistical algorithms, and data mining to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. It helps businesses anticipate trends, optimize decision-making, and mitigate risks. By analyzing patterns, AI can predict customer behavior, market trends, equipment failures, and financial risks. Industries like healthcare, finance, and retail leverage predictive analytics for personalized recommendations, fraud detection, and demand forecasting. AI enhances accuracy by continuously learning from new data, improving predictions over time. However, challenges like data bias, ethical concerns, and data privacy must be addressed. Overall, AI predictive analytics empowers organizations with data-driven foresight and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is predictive analytics ?
Predictive analytics involves using historical data and statistical techniques to forecast future events or behaviors.
2. How does predictive analytics differ from descriptive analytics ?
Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing past data, while predictive analytics aims to forecast future outcomes.
3. What types of data are used in predictive analysis ?
Both structured data (e.g., numerical) and unstructured data (e.g., text) are utilized.
4. Which industries benefit from predictive analytics ?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, marketing, and manufacturing widely use predictive analytics.
5. How accurate are predictive models ?
Accuracy depends on data quality, model selection, and the complexity of the problem.
Latest Posts
- All Posts
- Software Testing
- Uncategorized




Data Analytics
Getting job Is hard nowadays...but not with Bugspotter's Industry Oriented Training Programs
Categories
- Artificial Intelligence (5)
- Best IT Training Institute Pune (9)
- Cloud (2)
- Data Analyst (55)
- Data Analyst Pro (15)
- data engineer (18)
- Data Science (104)
- Data Science Pro (20)
- Data Science Questions (6)
- Digital Marketing (4)
- Full Stack Development (7)
- Hiring News (41)
- HR (3)
- Jobs (3)
- News (1)
- Placements (2)
- SAM (4)
- Software Testing (70)
- Software Testing Pro (8)
- Uncategorized (33)
- Update (33)
Tags
- Artificial Intelligence (5)
- Best IT Training Institute Pune (9)
- Cloud (2)
- Data Analyst (55)
- Data Analyst Pro (15)
- data engineer (18)
- Data Science (104)
- Data Science Pro (20)
- Data Science Questions (6)
- Digital Marketing (4)
- Full Stack Development (7)
- Hiring News (41)
- HR (3)
- Jobs (3)
- News (1)
- Placements (2)
- SAM (4)
- Software Testing (70)
- Software Testing Pro (8)
- Uncategorized (33)
- Update (33)





