What is API testing and why it is important ?

What is API Testing ?
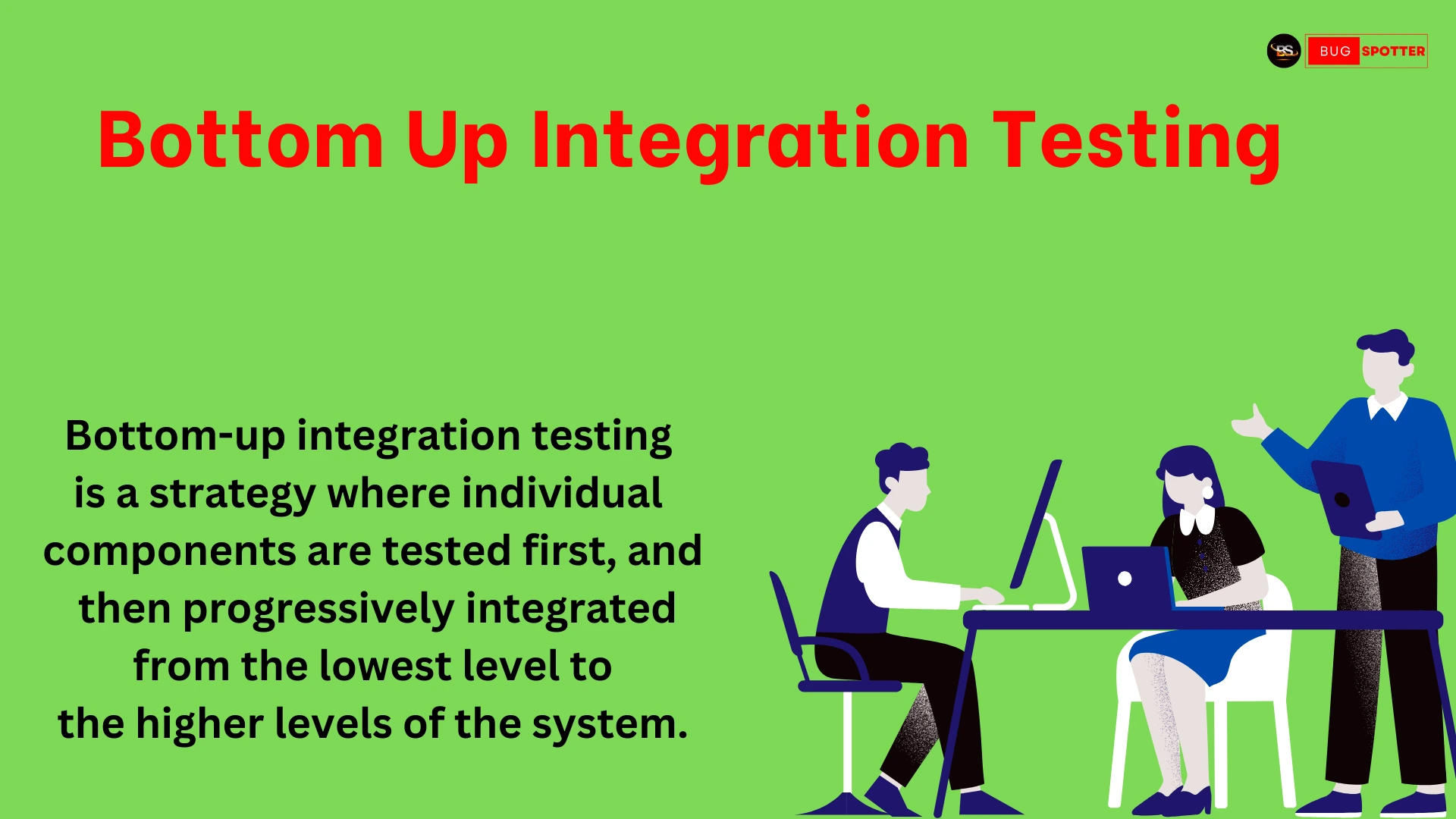
API testing is the process of checking if an API (a tool that allows different software systems to communicate with each other) works properly. It involves testing whether the API does what it is supposed to do, such as sending the right information, responding quickly, and handling errors correctly.
In simple terms, API testing is about making sure that when one program asks another program for data or to perform a task, it gets the correct response.
Key things tested in API testing include:
- Functionality: Does the API give the correct response when asked for something?
- Performance: Does the API work well even when many people use it at the same time?
- Security: Is the API protected from unauthorized access or attacks?
- Error Handling: Does the API handle mistakes properly and give clear error messages when needed?
What are the types of API testing ?
1. Functional Testing
Functional testing ensures the API performs its intended tasks correctly by verifying that each endpoint returns the expected results with valid inputs, and handles requests as per the defined requirements.
2. Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates how the API responds under normal and peak traffic conditions, checking for speed, resource usage, and responsiveness to ensure it can handle expected loads without degradation.
3. Security Testing
Security testing identifies vulnerabilities in the API, ensuring proper authentication, encryption, and protection against common threats like SQL injection and unauthorized access.
4. Load Testing
Load testing measures the API’s ability to handle a specified number of requests or traffic under normal conditions, ensuring it performs well under expected user loads.
5. Stress Testing
Stress testing pushes the API beyond its normal limits to assess its stability and recovery capabilities when subjected to excessive traffic or data, identifying breaking points and failure recovery.
6. Reliability Testing
Reliability testing ensures the API consistently performs correctly over time, detecting issues like memory leaks or performance degradation that could affect long-term operation.
7. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing checks the API’s functionality across different platforms, devices, browsers, and versions of software to ensure consistent behavior across various environments.
8. Regression Testing
Regression testing ensures that new changes or updates to the API don’t break existing functionality, verifying that previously working features still perform correctly after updates.
9. Fuzz Testing
Fuzz testing involves sending random or invalid data to the API to uncover vulnerabilities or unexpected behavior, helping identify security flaws or bugs that may be missed in normal testing.
10. Validation Testing
Validation testing ensures the API meets business requirements and user expectations, confirming that it provides the correct outputs and behaves as specified in the requirements.
Why API Testing is important ?
Ensures Correct Functionality
APIs are often used to allow different software systems or applications to communicate with each other. API testing ensures that the data is correctly exchanged, and the API does what it is supposed to do (e.g., returning the right data or performing actions correctly).
Improves Performance
APIs are frequently used in high-traffic applications. Testing ensures that the API can handle large numbers of requests, work quickly, and perform well under pressure. Without testing, an API might fail or slow down when the system is under load.
Detects Security Issues
APIs can be vulnerable to attacks like data breaches or unauthorized access. API testing helps identify security weaknesses and ensures the API is protected from malicious users and threats.
Reduces Errors and Bugs
API testing helps catch bugs early before the application goes live. If the API is not tested properly, it might return wrong data, break the application, or create problems when interacting with other systems. Catching these issues in testing helps prevent costly problems later.
Ensures Compatibility and Integration
Many modern applications rely on APIs to interact with third-party services (like payment gateways, social media platforms, etc.). Testing ensures that these external APIs work correctly and are integrated smoothly, so your app works properly with others.
Saves Time and Costs
Automated API testing can save time compared to manual testing and can be done regularly as the code changes. Catching issues early in the API’s lifecycle can also prevent expensive fixes later in development.
How API Testing Is Done ?
- Test Planning: Identify the API endpoints, define test cases, and set criteria for functionality, security, performance, and error handling.
- Send Requests: Use tools like Postman, SoapUI, or RestAssured to send requests (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to the API.
- Validate Responses: Check if the API returns the correct data, status codes (e.g., 200, 404), and handles errors properly.
- Security Testing: Ensure the API is secure by checking for vulnerabilities, unauthorized access, and data protection.
- Performance Testing: Test how the API performs under high load or heavy traffic conditions.
- Automated Testing: Automate repeated tests for efficiency and consistency, using tools or scripting languages.
- Report Results: Document the findings and share any issues or failures with the development team for fixing.
Latest Posts
- All Posts
- Software Testing
- Uncategorized




Categories
- Artificial Intelligence (5)
- Best IT Training Institute Pune (9)
- Cloud (2)
- Data Analyst (55)
- Data Analyst Pro (15)
- data engineer (18)
- Data Science (104)
- Data Science Pro (20)
- Data Science Questions (6)
- Digital Marketing (4)
- Full Stack Development (7)
- Hiring News (41)
- HR (3)
- Jobs (3)
- News (1)
- Placements (2)
- SAM (4)
- Software Testing (70)
- Software Testing Pro (8)
- Uncategorized (33)
- Update (33)
Tags
- Artificial Intelligence (5)
- Best IT Training Institute Pune (9)
- Cloud (2)
- Data Analyst (55)
- Data Analyst Pro (15)
- data engineer (18)
- Data Science (104)
- Data Science Pro (20)
- Data Science Questions (6)
- Digital Marketing (4)
- Full Stack Development (7)
- Hiring News (41)
- HR (3)
- Jobs (3)
- News (1)
- Placements (2)
- SAM (4)
- Software Testing (70)
- Software Testing Pro (8)
- Uncategorized (33)
- Update (33)





